Classical theory of employment believes that full employment exist under capitalist economy without the inflation.With the wage-price flexibility,there are the existence of some powers in the economy those who continuous the process of full employment.classical theory assume that full employment is a normal feature of the capitalist economy.
Say's law of market :- according to say's law of market "supply creates its own demand" . According to Say's production creates the market for the commodity. it's also said that the main source of demand is a factor-income.
factor income is a income which generates from the process of production.Factors are land,labour and capital which gives the income as rent,wages and interest respectively.
By using factor- income(land-rent,labor-wages,capital-rate of interest ) people demand for the products.
Relationship of savings and investment with rate of interest.
Savings and rate of interest :-There is a positive relationship between the Savings and the rate of interest.That is, if rate of interest increases then savings also increases and vice versa.
Investment and rate of interest :- there is a negative relationship between the investment and rate of interest.That is,if rate of interest increases then investment decreases and vice versa.
Explanation with diagram
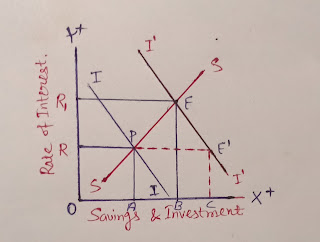 |
| Relationship b/w savings, investment and rate of interest |
Here,we have saving and investment at x axis and rate of interest at y-axis
At initial point P, Savings and investment are equals to each other at rate of interest"R".Suppose,investment increases OA to OC at "R" but here investment is more than the savings that is OA< OC(I>S) ,but according to the classical this condition(I>S)never hold in the economy.
Acc. To classicals, to attain this condition (S=I) in the economy,rate of interest will increases from R to R1 and equilibrium find itself at E.
Measurements of classical theory of employment:-
Demand for labour :- Demand for labour depends upon the real- wages but it is also depend upon the MPP ( marginal physical productivity)
D(L)=f(w/p). D(L)=demand for labor
w=nominal wages
p=rate of inflation
w/p=real wages
there is a negative relationship between the demand for labour and real wages.when real wages decreases the demand for labour increases and vice versa.
An entrepreneur increases his demand for labour till that point where MPP (marginal physical productivity) is equal to the real wages.
Under the measurement of demand for labour diminishing marginal returns also exist in the production process.
Supply of labour :- supply of labour also depend upon the real wages.
S(L)=f(w/p) S(L) =supply of labour
w/p=real wages
w=nominal wages
p=rate of inflation
There is a positive relationship between the supply of labour and real wages. That is, if real wages increases then supply of labour is also increases and vice versa.
FLEXIBILITY OF WAGES ,INTEREST AND PRICES
prof. Pigou has explained this with the help of the following equation
N=QY/W.
N stands for the level of employment,
QY:- stands for the part of the national income which is paid as wages
W :- stands for the money wage rate
Here we wil understand with this,with the help of diagram
 |
| Wage,price flexibility |
We have taken employment at x-axis and wage rate at y axis
at wage rate OW(2) the demand for labour is more than the supply of labour.On the other hand at wage rate OW(1) the supply of labour is more than the demand for the labour.both situations are shows dis-equilibrium between the demand for labour and supply of labour.
At the wage rate OW the supply of labour and the demand for the labour is equal to each other at ponit E,so E is the point of equilibrium.
wage rate would be flexible between W2 and W1.
Wage rate will be set up more than W2 but less than W1 in the economy.

.png)






No comments:
Post a Comment